China Tariffs Impact: How They Could Affect U.S. Economy
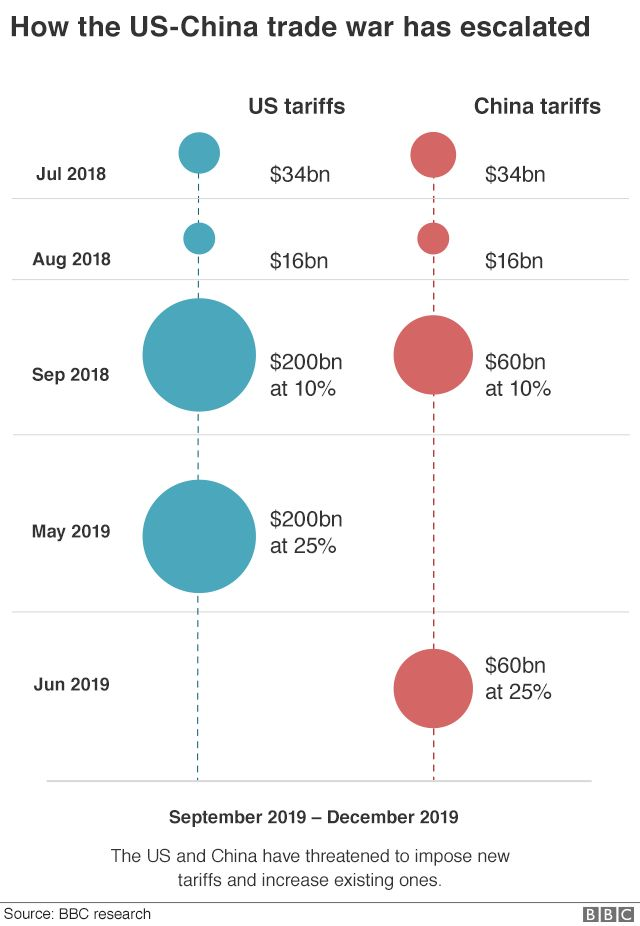
The impact of China tariffs has become a pivotal concern for both the U.S. economy and China trade relations as we approach a renewed era of tariff imposition. President Trump’s proposal of steep tariffs could destabilize Beijing’s economy, which is already grappling with a faltering housing market and lackluster consumer demand. Economists warn that such tariffs might not only elevate prices for American consumers but also trigger significant supply chain disruptions across various industries. Further complicating matters, these tariffs could inadvertently allow Beijing to strengthen ties with U.S. allies who find themselves caught in the crossfire of trade hostilities. The looming uncertainty surrounding these potential tariffs demands a closer examination of how they might reshape the economic landscape on both sides of the Pacific, affecting everything from manufacturing to international relations.
Exploring the ramifications of tariffs on imports from China reveals critical tensions in trading dynamics between the United States and its principal trade partner. As new protective measures are discussed, the potential fallout for the U.S. and its allies could be profound, signaling a shift in global economic strategies. Analysts emphasize that these import duties could have collateral effects not just on financial markets but also on diplomatic relations, as countries reassess their affiliations and trade dependencies. At the same time, the search for alternative manufacturing hubs may accelerate as companies look to buffer their supply chains against unforeseen disruptions. As the world watches closely, the intricate dance of trade negotiations may ultimately redefine the landscape of international commerce.
Understanding the Consequences of China Tariffs on the U.S. Economy
The potential imposition of high tariffs on imports from China could lead to significant unintended consequences for the U.S. economy. Foremost among these concerns is the likelihood of increased prices on various consumer goods. Items such as electronics, apparel, and household goods, which often have components sourced from China, may see price hikes, resulting in less purchasing power for American consumers. Additionally, a surge in tariffs could lead to supply chain disruptions, complicating logistics and inventory management for companies reliant on Chinese manufacturing. This ripple effect could ultimately reduce market competitiveness, depress consumer spending, and stymie overall economic growth.
Moreover, the tariffs could exacerbate existing tensions in U.S.-China trade relations, possibly inciting a retaliatory response from Beijing. Should China opt to levy tariffs on American exports, particularly agricultural products such as soybeans or pork, U.S. farmers could face dire consequences, including decreased sales and financial strain. This chain of events could tarnish relations not only between the U.S. and China but also affect the broader network of U.S. allies, who might be caught in the crossfire of a prolonged trade war. The economic effects could, therefore, extend far beyond direct transactions between China and the United States.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of China tariffs on the U.S. economy?
The impact of China tariffs on the U.S. economy can be significant, potentially increasing prices for American consumers and leading to supply chain disruptions. Higher tariffs may result in manufacturers facing higher costs for imported goods, which can ultimately affect retail prices. Additionally, such tariffs could strain U.S.-China trade relations.
How are China tariffs affecting trade relations between the U.S. and China?
China tariffs are straining trade relations between the U.S. and China, as they create a hostile environment for trade. These tariffs may encourage China to strengthen ties with other global partners, potentially reducing its reliance on U.S. markets. This shift could lead to a reconfiguration of global trade alliances.
What are the potential effects of Trump tariffs on China’s economy?
Trump tariffs could significantly harm China’s economy by hitting its crucial export sector, particularly as the U.S. remains a major market for Chinese goods. The imposition of high tariffs can exacerbate existing economic challenges in China, including market slowdowns and reduced consumer demand.
Could China tariffs lead to supply chain disruptions in the U.S.?
Yes, China tariffs could lead to supply chain disruptions in the U.S. as companies who rely on Chinese imports may face delays and increased costs. This disruption can affect the availability of goods and manufacturing efficiency in various sectors, prompting companies to seek alternative suppliers.
How might Beijing respond to increasing tariffs from the U.S.?
Beijing may respond to increasing tariffs from the U.S. by seeking to diversify its trade partnerships and strengthen economic ties with other nations. Additionally, China might implement domestic economic measures to mitigate the impact of tariffs on its economy and may also engage in negotiations to address trade tensions.
What role do tariffs play in the current U.S.-China trade relations?
Tariffs play a central role in the current U.S.-China trade relations, often serving as a focal point of tension. They represent a tool used by the U.S. to address trade imbalances and halt practices perceived as unfair, while China views these tariffs as harmful to bilateral relations and its economic stability.
Are there any countries positioned to benefit from reduced Chinese imports to the U.S.?
Countries like Vietnam and India may benefit from reduced Chinese imports to the U.S., as businesses look for alternative manufacturing locations. However, these countries face their own challenges in matching the scale and efficiency of Chinese production capabilities.
How do tariffs impact American consumers?
Tariffs can lead to increased prices for American consumers as businesses typically pass on higher costs of imported goods. This increase can affect a wide variety of products, leading to inflationary pressures within the economy.
What are the long-term implications of China tariffs on global trade?
The long-term implications of China tariffs on global trade could include a shift in supply chains, as countries seek to reduce their dependence on China. This restructuring may lead to new trade partnerships and can significantly alter the dynamics of international trade.
How do tariffs influence China’s strategy in global markets?
Tariffs influence China’s strategy in global markets by pushing it to seek new trade opportunities and reinforce existing partnerships, particularly in regions like Southeast Asia and Europe. The need to minimize the impact of U.S. tariffs may drive China to diversify its export markets and develop its domestic economy.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| China’s Economy Under Strain | China already faces a weak housing market and declining consumer demand. |
| Potential U.S. Tariffs | President-elect Trump proposed tariffs of 25% on goods from Canada and Mexico and 10% on Chinese imports. |
| Impact on American Consumers | Higher tariffs could increase prices for U.S. consumers and disrupt supply chains. |
| China’s Export Challenge | Tariffs may significantly hamper China’s exports to the vital U.S. market, affecting its economy. |
| Global Trade Relations | Tariffs might strengthen China’s ties with other countries, shifting alliances in international trade. |
| Alternative Suppliers | Countries like India and Vietnam may struggle to fill the gap left by reduced Chinese imports. |
| Opportunities for China | Broad tariffs could push China to negotiate stronger engagements with Europe and other allies. |
Summary
The impact of China tariffs on the U.S. economy could lead to significant price increases for consumers and uncertainty in international trade relationships. As new tariffs are imposed, not only would American consumers face higher costs, but China might also find new opportunities to strengthen alliances with its traditional allies. Moreover, this situation poses a risk for the U.S. to inadvertently create a more unified front among nations that are facing similar trade challenges, potentially resulting in long-lasting implications for U.S.-China relations.



